)
English Language Learning
How are students identified as EL?
EL (English Learner) students are identified through a home langauge survey and the AZELLA. If the home language survey indicates a language other than English for any one of the three responses, then the student is administered the AZELLA. If the student does not achieve proficiency on the AZELLA, the student is identified as an EL and is eligible to receive EL services.
When are students assessed on AZELLA? How many times per year are they assessed?
Students that score less than proficient on the AZELLA test are eligible for EL services. Students that are eligible for EL services will be administered the Spring AZELLA reassessment annually until student scores proficient.
Are EL Students required to take standardized state tests?
Yes. EL students are required to participate in all state-mandated testing.
What are EL services?
Arizona requires school districts and charter schools (otherwise known as Local Education Agencies or LEAs) with English learner (EL) students to provide English language development (ELD) instruction using a structured English immersion (SEI) model. Arizona uses the Language Development Approach.
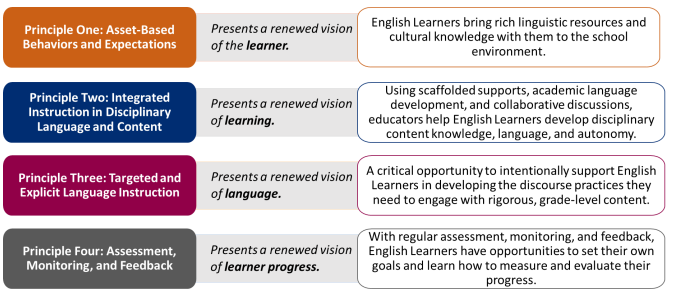
EL Instruction consists of Targeted Instruction and Integrated Instruction
Targeted & Explicit Langauge Instruction
- Focuses on explicit, systematic, and sustained English language instruction.
- Meets the scheduled minutes in alignment with the selected SEI Model(s) at the site.
- Evidence includes, but is not limited to:
- detailed and labeled master schedules,
- labeled classroom schedules,
- individual student schedules (specific to departmentalized and secondary levels).
- Groups ELs alongside their EL peers only.
- Targeted ELD should be comprised of ELs in only one grade level and English proficiency level to the extent possible. When lower numbers indicate a need, student groups may contain students within two adjacent proficiency levels and/or in more than one grade level within the same ELP Standards band (grade bands: K, 1, 2-3, 4-5, 6-8, & 9-12).
- Evidence includes class lists (with ELs’ proficiency levels noted) demonstrating the homogenous instructional groups.
- Is driven by Performance Indicators (PIs) of the ELP Standards and assessment of learning is directly aligned to the PIs.
- Evidence would be the demonstration of planning for ELs using PIs from the ELPS to direct the teaching, learning, and assessing. Could include, but is not limited to, lesson plans, agendas, plan outlines, posting of PIs in classroom, etc.
- Meets the diverse language needs of ELs.
- Builds into and from what is happening in other academic settings.
- Utilizes academic language and provides opportunities for students to develop academic discourse.
- Must be provided by an appropriately certified teacher with an SEI, ESL, or BLE Endorsement, or completed SEI coursework.
- A teacher may allow a student to utilize independent software to supplement instruction for up to 40% of the selected SEI Model’s Targeted Instructional block of time to reinforce the instruction provided by the teacher. The expectation is that the independent software will address the EL’s individual language needs. It may be utilized as part of small group instruction in which the teacher is monitoring the progress and follows-up with the learning.
Integrated Instruction
All educators share the responsibility for designing instruction that integrates language and literacy development with content learning. This is accomplished by using content standards to plan instruction along with the English Language Proficiency Standards to support differentiation by language proficiency level. Integrated instruction:
- Focuses on access to grade-level content and development of discipline-specific academic language.
- Meets the scheduled minutes in alignment with the selected SEI Model(s) at the site.
- Evidence includes, but is not limited to:
- detailed and labeled master schedules,
- labeled classroom schedules,
- individual student schedules (specific to departmentalized and secondary levels).
- Groups ELs alongside their non-EL peers.
- Evidence includes class rosters (with ELs’ proficiency levels noted) demonstrating the mixed groups for content instruction.
- Is driven by content-area standard(s) and assessment of learning is grounded in the content-area standard(s).
- Utilizes Performance Indicators from the ELP Standards to support language to access content learning.
- Evidence would be anything demonstrating planning for ELs using PIs from the ELPS to direct the teaching, learning, and assessing. Could include, but is not limited to, lesson plans, agendas, plan outlines, posting of PIs in classroom, etc.
- Differentiated scaffolds are present in the lesson.
- Scaffolds allow for students to access and engage with content.
- Occurs within one or more content areas (e.g., ELA, science, art, math, etc.).
- Must be provided by an appropriately certified teacher with an SEI, ESL, or BLE Endorsement, or completed SEI coursework.
- The SEI Models require daily Integrated Instruction is to be delivered by an SEI /ESL/BLE endorsed teacher. During Integrated Instruction, ELs will be participating in the content learning alongside non-ELs and therefore will not be receiving instruction via independent language instructional software at that time.
Questions?
Contact your Federal Projects Specialist @ 623-876-7072